Window-to-China
Overview of last view News
China’s National Institute of Metrology (NIM) develops monoclonal antibody reference material for COVID-19, and antibody and nucleic acid test kits from China are already being exported
Since the outbreak of the epidemic, immunoassays based on IgM antibody and IgG antibody of the COVID-19 patients have become an important supplement to nucleic acid-based detection.
Two new antibody reference materials developed by the NIM were now approvaed as national reference materials by the State Administration for Market Regulation.
As of March 16, a total of 11 nucleic acid detection reagents and eight antibody detection reagents for the COVID-19 were approved in China. According to a report by Japan’s Nikkei Biotech, some test kits developed by Tsinghua University, Sichuan University, Xiamen University, Xiamen University of Technology and Chongqing Medical University have already received CE certification and are exported to more than 10 countries, including Italy, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands.
Xinhua news release, March 23, 2020
Nikkei Biotech news release, March 18, 2020
CMDA approves test chip for multiple respiratory viruses
The virus chip was jointly developed by West China Hospital affiliated to Sichuan University, Tsinghua University and a Chengdu-based biotech company, Boao Jingxin Biotechnology Co. With secretion samples collected from patients’ noses and throats, the chip detects six common respiratory viruses including the novel coronavirus all at once within 1.5 hours. Each chip allows the detection of 16 samples in a single assay at the same time.
CAS news release, February 24, 2020

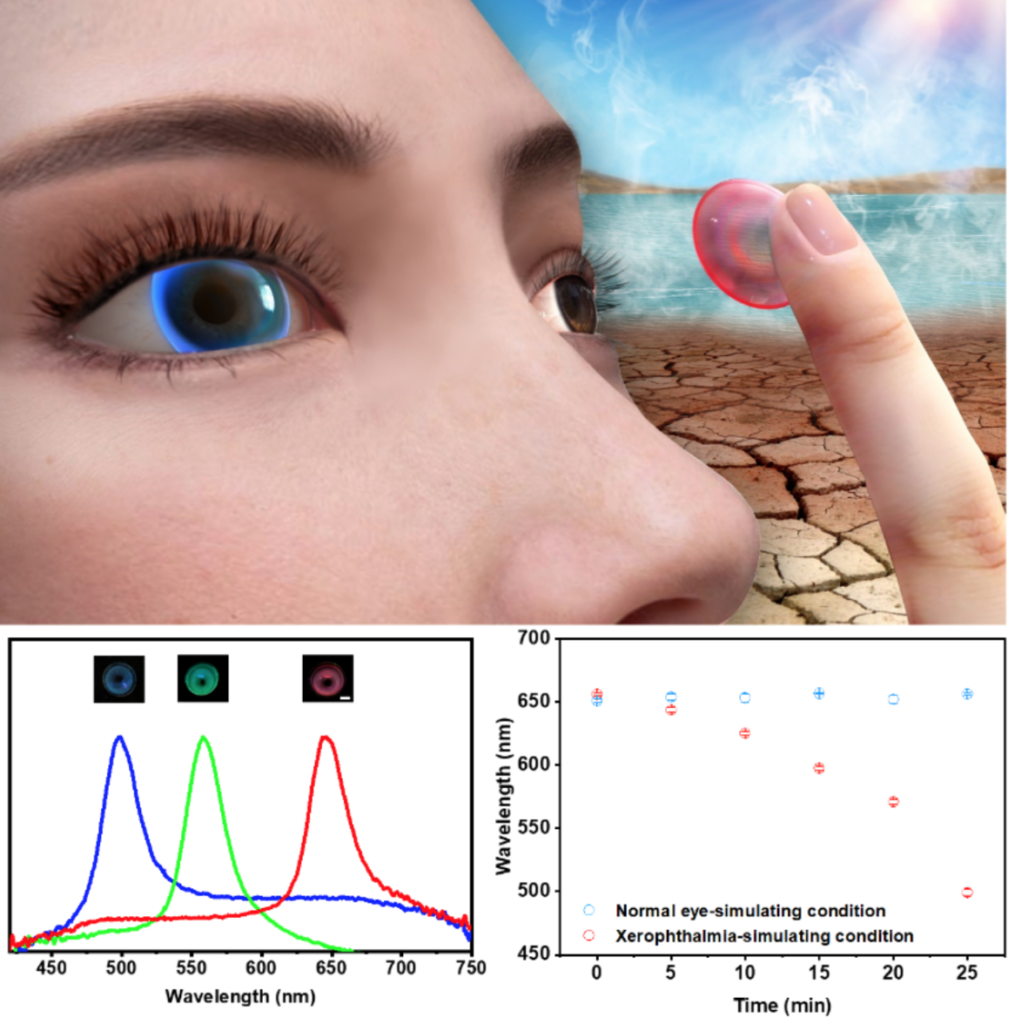
Smart contact lenses for point-of-care eye health monitoring: CAS Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technologies
The group of DU Xuemin has developed a contact lense made from a poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) hydrogel matrix which features periodic nanostructures, resulting in bright, tunable structural colors ranging from red to green to blue. The spacing of periodic nanostructures within the pHEMA hydrogel are sensitive to changes in moisture and pressure, leading to real-time color changes. Based on these features, the ‘smart’ contact lens can monitor xerophthalmia and high intraocular pressure. Under normal conditions, its color will not change over time, while its color changes from red to blue in the xerophthalmia-simulation condition in about 25 minutes. In addition, a linear decrease in the wavelength of the reflectance peak of the “smart” contact lens is observed when human intraocular pressure changes in the pathological range.
CAS news release, February 19, 2020
CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Technology (DICP) develops nanoreactor for electrochemical nitrogen fixation
The teams of LIU Jian at CAS DICP and LIANG Kun at the Institute of Superconducting and Electronic Materials, University of Wollongong, Australia, have tried defect engineered iron doping for electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation. Using an iron-doped Wolfram18049 catalyst in a nanoreactor, they achieved 24.7 μg / (h * mgcat) yields of NH3 and 20.0% Faraday efficiency at ambient temperature.
CAS news release, February 27, 2020
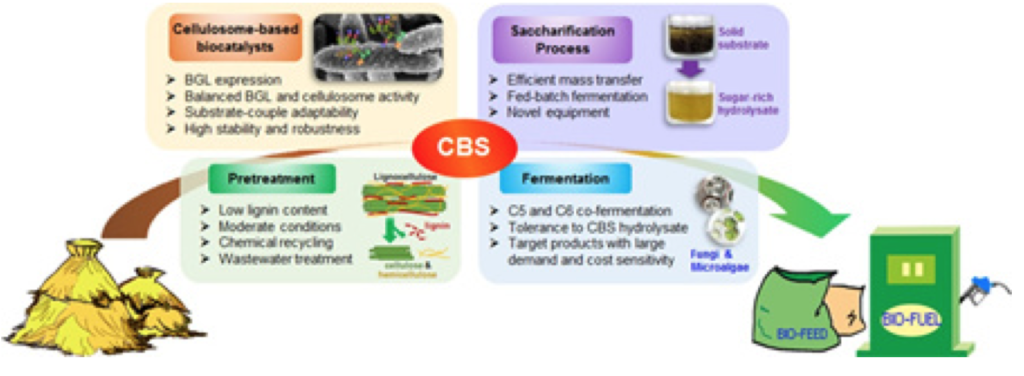
CAS QIBEBT reviews lignocellulose biotransformation by “consolidated biological saccharification” (CBS)
The team of CUI Qiu at CAS Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Process Technology (QIBEBT) has reviewed a process for biomass to sugar conversion developed in their own and other groups. The strategy employs cellulosome-producing microorganisms as a biocatalyst to enhance lignocellulose solubilization and produces lignocellulose-derived fermentable sugars as a platform product for fermentations aiming at various products.
CAS news release, March 3, 2020
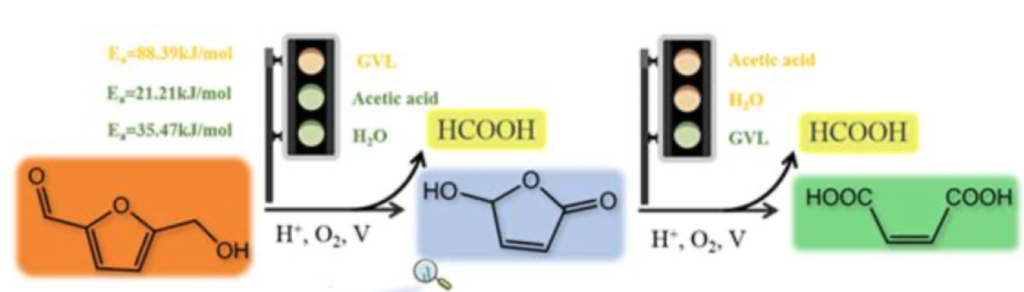
Shanxi Institute of Coal Chemistry finds new “green route” to maleic anhydride
The team around HOU Xianglin and DENG Tiansheng of the Shanxi Provincial Biorefinery Engineering Technology Research Center at the above institute started out with hydroxymethylfurfural,an intermediate derived from monosaccharides such as glucose, and used used a graphene oxide-supported metal vanadium as a catalyst for oxidation. The best solvents were acetic acid and water.
Maleic anhydride is an important chemical intermediate, e. g., for the synthesis of polymers.
CAS news release, March 6, 2020
China invests heavily in 5G infrastructure
According to the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), China expects over 550,000 5G base stations to be put in operation by the end of 2020. Prefecture-level cities are expected to achieve continuous outdoor connection of the 5G network within this year, with key areas in counties and townships. During the battle against the novel coronavirus, telemedicine and smart robots using 5G technology have come from trials into front-line practices, while remote office solutions and online teaching also contribute to quarantine efforts as well as the resumption of work and production. With a solid industrial foundation and maturing commercial products, the CAICT is expecting China’s 5G industry to directly create over 3 million jobs as of 2025.
CAS news release, March 5, 2020
China’s spallation neutron source reaches design beam power
The neutron diffraction device, operated by CAS Institute of High Energy Physics and located in Dongguan, Guangdong Province, has reached its design beam power of 100 kW. In September 2018, the CSNS ran with a power of 20 KW. Its operating beam power had reached 50 KW in January 2019 and 80 KW in October 2019.
With its beam power gradually increasing, the CSNS exceeded its user operation target in 2019 with a total of 4,576 hours.
CAS news release, March 5, 2020
Improved ecosystem at China’s largest saltwater lake, Qinghai lake
After launching a project in 2008 with expenditures of 226 million US$, the 4.500 km2 lake in Qinghai Province increased in size, and bird and fish species increased.
CAS news release, March 4, 2020

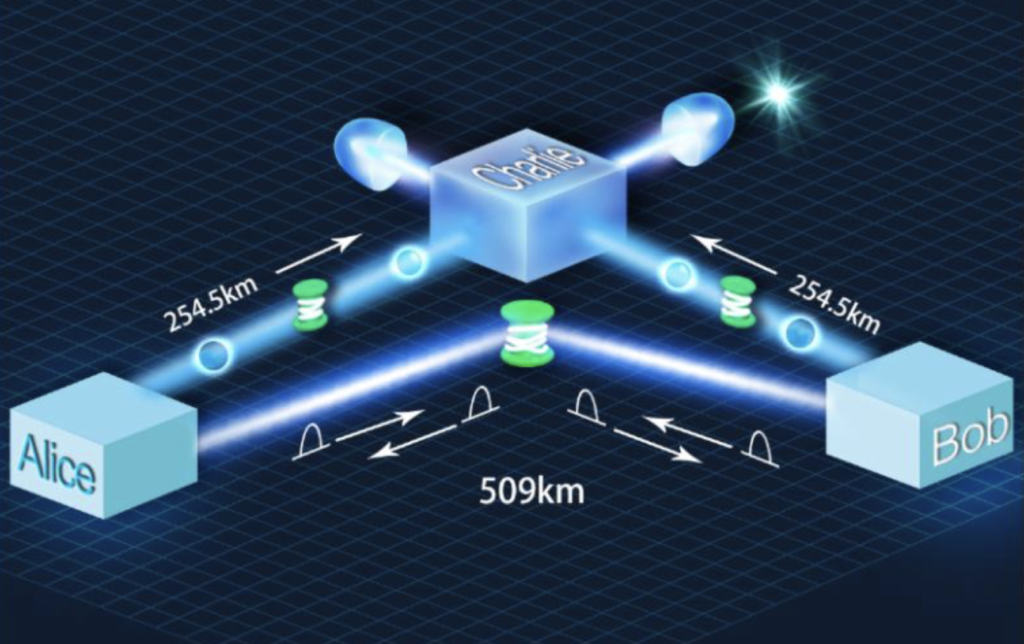
China University of Science and Technology achieves 500 km of ground-based quantum key distribution
In long-distance practical applications of quantum key distribution (QKD), channel loss is the most serious limiting factor. The existing measurement equipment-independent quantum key distribution (MDI-QKD) uses a two-photon composite event as an effective detection event, so that its secure coding rate decreases linearly with the channel attenuation.
In two related studies, PAN Jianwei and colleagues at the University of Science and Technology in China developed a time-frequency transmission technology and a laser injection locking technology based on a “send-not-send” TF-QKD and a PM-QKD. The wavelength locks of two independent remote lasers are the same, and the additional phase reference light is used to estimate the relative phase drift of the fiber. Combined with the high counting rate and low noise single photon detector developed by CAS Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, QKD’s safe coding distance was finally pushed to over 500 kilometers in the laboratory.
CAS news release, March 4, 2020
Qingdao hospital introduces two “robot nurses” for food delivery in an new pneumonia intensive station.
The two smart medical robots operated by a 5G system carry out automatic disinfection, inhalation of waste air, sanitization, and automatic food and medicine delivery services in isolated areas. They can deliver meals to a designated room within 1-2 minutes, reducing the probability of cross-infection between healthcare workers and isolated observers.
Xinhuanet, February 26, 2020

Group at CAS DICP establishes photocatalytic method to convert polyols and sugars into methanol and syngas
The group of WANG Feng at CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics have established a method to convert biomass-derived polyols and sugars into methanol and syngas (CO+H2) via UV light irradiation at room temperature. The bio-syngas could be further used for the synthesis of methanol. Cellulose and even raw wood sawdust could be converted into methanol or syngas after hydrogenolysis or hydrolysis pretreatment.
The researchers also found that Cu dispersed on titanium oxide nanorods (TNR) rich in defects effectively promoted selective C-C bond cleavage that produced methanol. Using this process, methanol was obtained from glycerol with co-production of H2. A syngas with CO selectivity up to 90% in the gas phase was obtained by controlling the energy band structure of Cu/TNR.
CAS news release, February 2, 2020
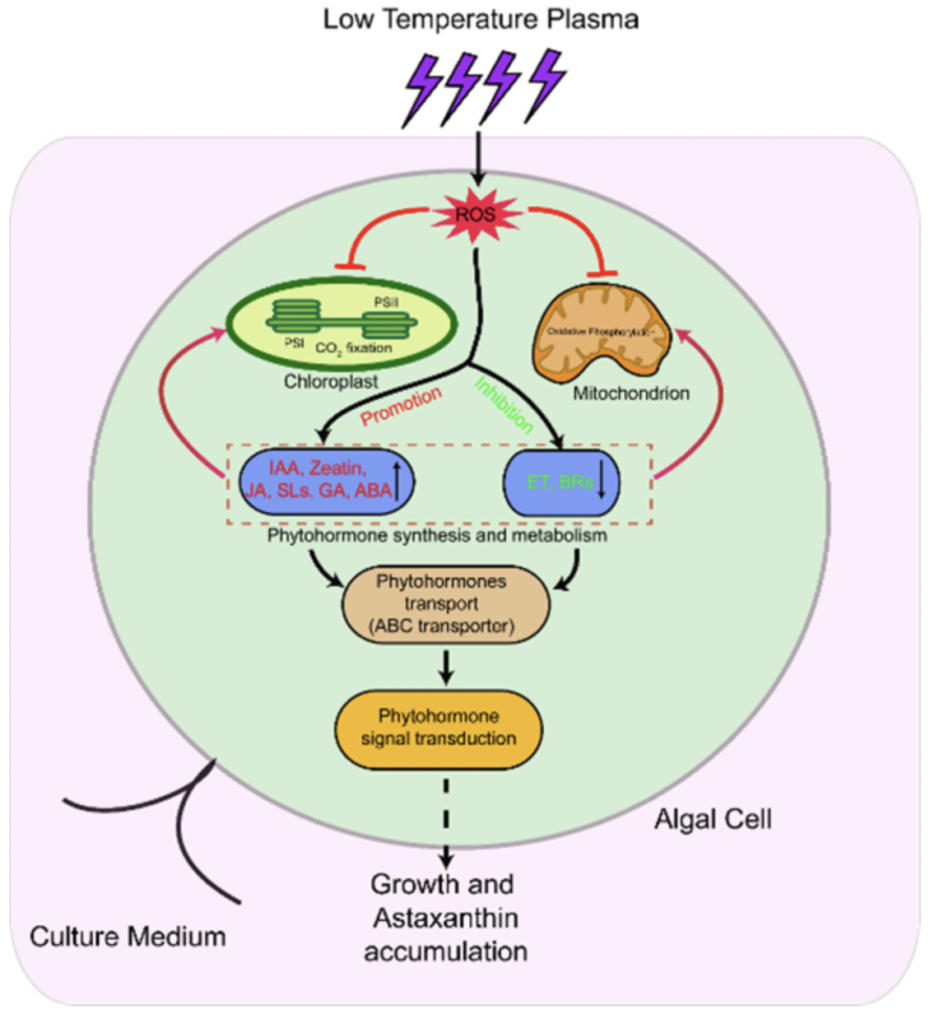
Low-temperature plasma stimulates astaxanthin productin in Hematococcus: CAS Hefei Institute of Material Sciences
QING Huang and colleagues at the institute have found that low-temperature plasma can stimulate the growth of Haematococcus pluvialis and astaxanthin accumulation. Transcriptomics analysis revealed that low-temperature plasma can regulate the synthesis, metabolism, and transport of hormones such as indole-3-acid (IAA), zeatin, and gibberellin (GA) through oxidative stress mechanisms, leading to enhanced growth and higher production of astaxanthin
CAS news release, February 28, 2020
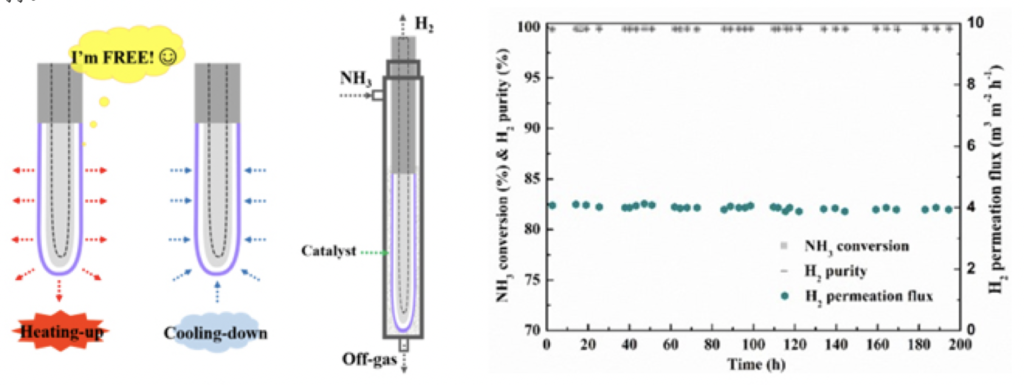
CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics develops Pd composite membrane for ammonia to hydrogen fuel cells
Researchers at the CAS DICP have developed a stainless steel reactor with a palladium composite membrane which allowed ammonia decomposition to hydrogen under long-term stable operation for 2000 h. Combination with an ammonia decomposing Ru/MgO catalyst in a membrane reactor reduced the temperature for complete ammonia decomposition from above 748 K to 673 K at stable operation for 200 h.
CAS news release, February 13, 2020
142 Seawater desalination projects in China completed by the end of 2018
According to the Ministry of Natural Resources, by the end of 2018 142 seawater desalination projects were completed, with a scale of 1,121,700 tons per day. The largest single unit of the seawater desalination project is 200,000 tons per day. Technology mainly adopts reverse osmosis and multi-stage flash seawater desalination. In the Northern Ocean Economic Zone around Tianjin, Shandong and Hebei, projects focus on large-scale industrial seawater desalination for the electricity and steel industry. In the eastern and southern marine economic zones, there are many private seawater desalination projects on remote islands, mainly distributed in Zhejiang and Guangdong, with 100-ton and 1,000-ton projects. In addition to seawater desalination, seawater used for cooling by the end of 2018 increased to 13,156 million tons.
Japan JST China news, February 10, 2020
Chinese-French oceanographic CFOSat satellite put into service
After 8 month in-orbit-testing, the oceanography satellite co-developed by China and France and launched in October 2018 was now put into service. The satellite acquires high-accuracy remote sensing data with its scatterometer and wave spectrometer, and can conduct high-resolution observations of ocean surface wind fields, which have been applied in monitoring typhoons, hurricanes, and the Arctic and Antarctic sea ice. The observation data will play an important role in global marine environment monitoring, disaster prevention and tackling climate change.
Xinhua news release, February 21, 2020
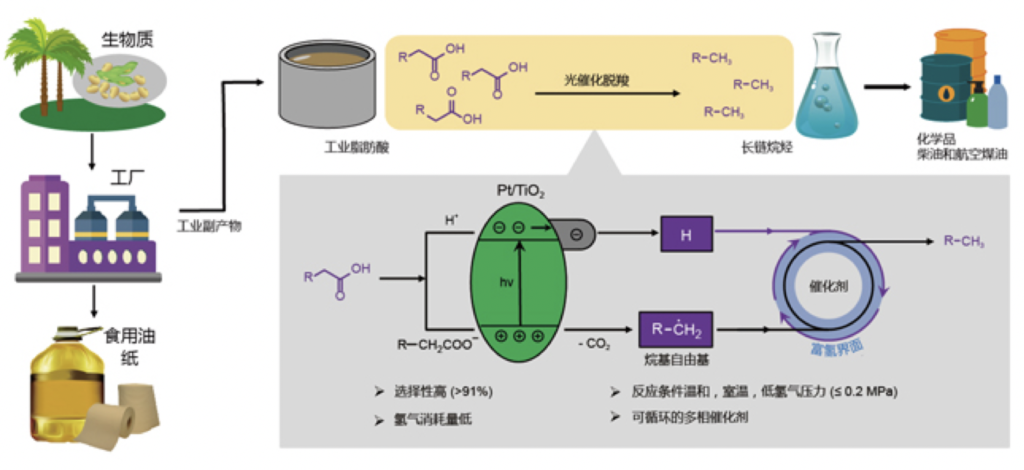
CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics converts biomass fatty acids to long-chain alanes under mild conditions
Researchers around WANG Feng from the Bioenergy Chemicals Research Group have developed a photocatalytic decarboxylation procedure to convert long-chain fatty acids to alkanes under mild conditions. They used low-value long-chain fatty acids from a bio-oil refining process and paper industry production. Through catalytic deoxygenation, long-chain alkanes where obtained, which were used to produce diesel and aviation kerosene. At room temperature, low hydrogen pressure (≤0.2 MPa) and UV light, the yield was > 90%.
CAS news release, February 20, 2020
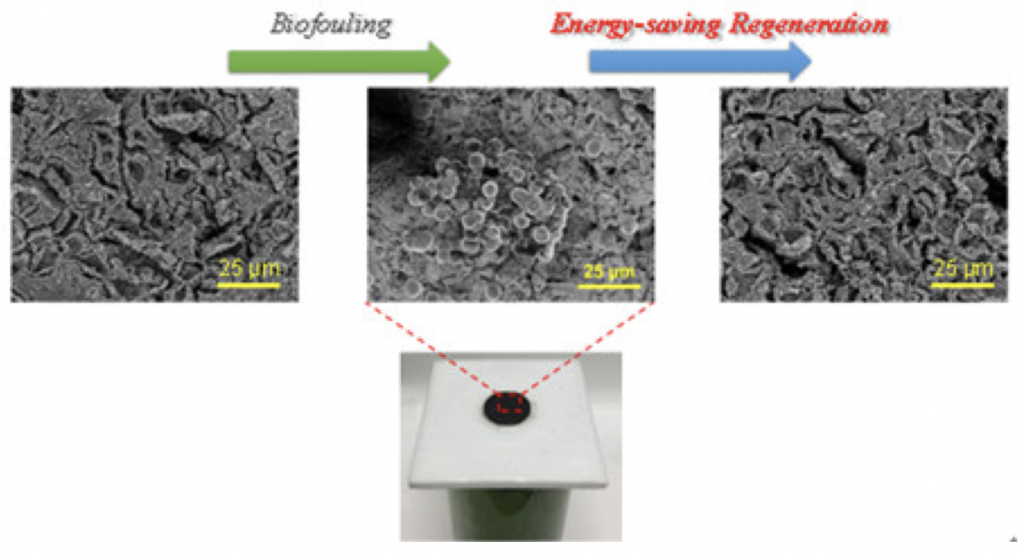
CAS QIBEBT develops perovskite oxide-based porous membrane for solar-driven evaporation and regeneration
Biological pollutants such as algae, or organic pollutants cause pollution of photothermal films in solar-driven water evaporation. They can be removed by high-temperature degradation, resulting in considerable energy consumption. The group around JIANG Heqing at CAS Qingdao Institute of Bio-Energy and Environmental Biotechnology (QIBEBT) has used the catalytic and photothermal properties of cobalt-based perovskite for a multifunctional perovskite oxide porous membrane. In tests using algae and melamine as pollutants, the La0.7Sr0.3CoO3 (LSCO) porous membrane significantly reduced the combustion decomposition temperature of the pollutants attached to it, reducing the energy consumption of the porous membrane during the combustion process. Performance could be almost completely restored after multiple membrane regeneration cycles.
CAS news release, February 19, 2020
Chinese specialists explore potential of TCM drugs in treatment of Coronavirus infections
According to a press conference of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, China’s think-tank, on February 18, in-vitro experiments with 54 TCM pharmaceuticals and related drugs at a Guangzhou Hospital have shown that 5 among these drugs suppressed Coronavirus infections and had anti-inflammatory effects. They are hoped to complement treatment by Western medicine, at least for mild cases of infection.
Japan JST China news, February 19, 2020
Team at CAS China’s University of Science and Technology develops “Raman picoscopy”
HOU Jianguo and colleagues have improved low-temperature (liquid helium) ultra-high vacuum tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy to fine-tuned the localized plasmon field at the tip height to a spatial resolution to 1.5 Angstroms of single chemical bonds. In space, a complete spatial imaging pattern of various intrinsic vibration modes of a molecule was obtained. The scientists propose “scanning Raman picoscopy” as a new method for visually constructing molecular structures based by molecular imaging patterns at Angstrom resolution.
CAS news release, February 13, 2020
